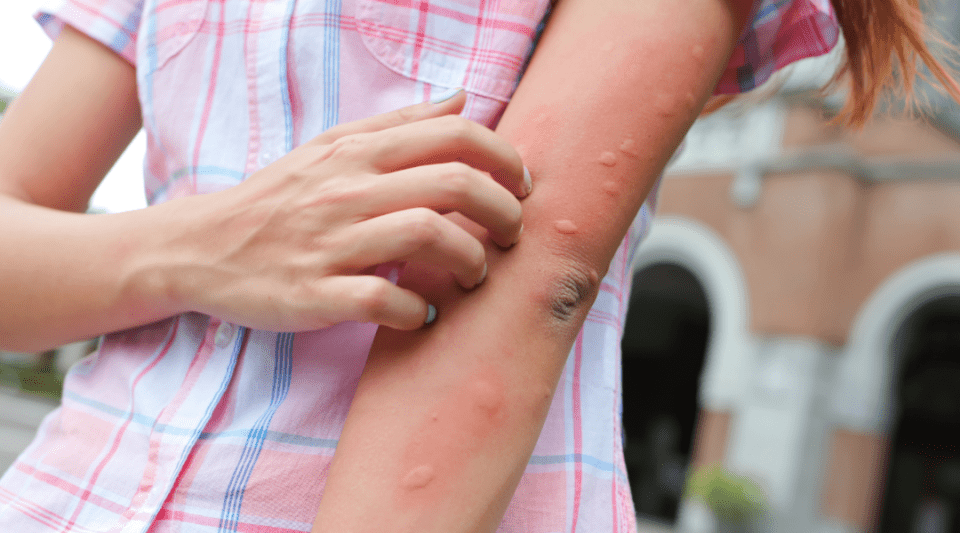
It is often impossible to know for sure which insect was responsible, but there are clues that can help point us in the right direction. It is also important to know when a bite is just a nuisance and when it may indicate an allergic reaction requiring medical attention.
How to recognise different insect bites:
- Mosquitoes: Their bites are common, often appear randomly and tend to cause less inflammation. They usually cause redness, itching and a small bump or welt.
- Spiders: Their bites typically result in single, more inflamed lesions, which may sometimes become necrotic (with scabs or bedsores). Occasionally, you may notice two red dots where the spider's fangs entered the skin.
- Fleas and bedbugs: These bites are distinctive because they appear in a line. They are known as 'breakfast, lunch and dinner', as these insects crawl along the skin biting several times along the way. They are usually found in the morning, as the bites occur at night.
- Bees and wasps: Their stings are often more painful and can cause noticeable localised swelling. In some cases, they can also cause more severe allergic reactions.
How can you tell if it's an allergic reaction?
It is normal for any bite or sting to cause redness, swelling and itching in the affected area. However, this does not necessarily mean that you are allergic. Most reactions are local and irritating, but not dangerous.
An allergic reaction occurs when the immune system overreacts to the insect’s venom or saliva. This response, known as an adaptive immune response, means that the body has been previously exposed to the substance and has developed defences against it. In these cases, the reaction may spread beyond the bite area.
It is therefore essential to know how to identify a severe allergic reaction, also known as anaphylaxis, as it can be life-threatening. Symptoms include:
- Swelling in areas away from the bite, such as the lips, eyes or throat.
- Difficulty breathing or a feeling of tightness in the chest.
- Dizziness or loss of consciousness.
- Widespread hives or rash.
If you experience any of these symptoms, seek emergency medical attention immediately.
What should you do if you are bitten or stung?
- Wash the affected area thoroughly with soap and water to prevent infection.
- Apply a cold compress to reduce swelling.
- Use antihistamine creams or topical corticosteroids if the itching is severe.
- Take oral antihistamines if the discomfort worsens.
- Monitor the evolution: if the redness or swelling spreads rapidly or general symptoms appear, seek medical help.
While many bites and stings are uncomfortable, in most cases they do not pose a major risk. Being able to recognise bite patterns can provide clues about the type of insect that caused the bite or sting, although this cannot always be confirmed. The most important thing is to monitor your body's reaction and respond quickly if warning signs appear. Understanding these differences enables us to stay calm and recognise when we really need to be concerned.
MORE INFORMATION: