As digital technologies evolve, AI is becoming a key tool for improving the speed and efficiency of diagnoses, opening up a range of possibilities in the field of precision and personalized medicine.
The Role of Machine Learning and Neural Networks in Diagnostic Imaging
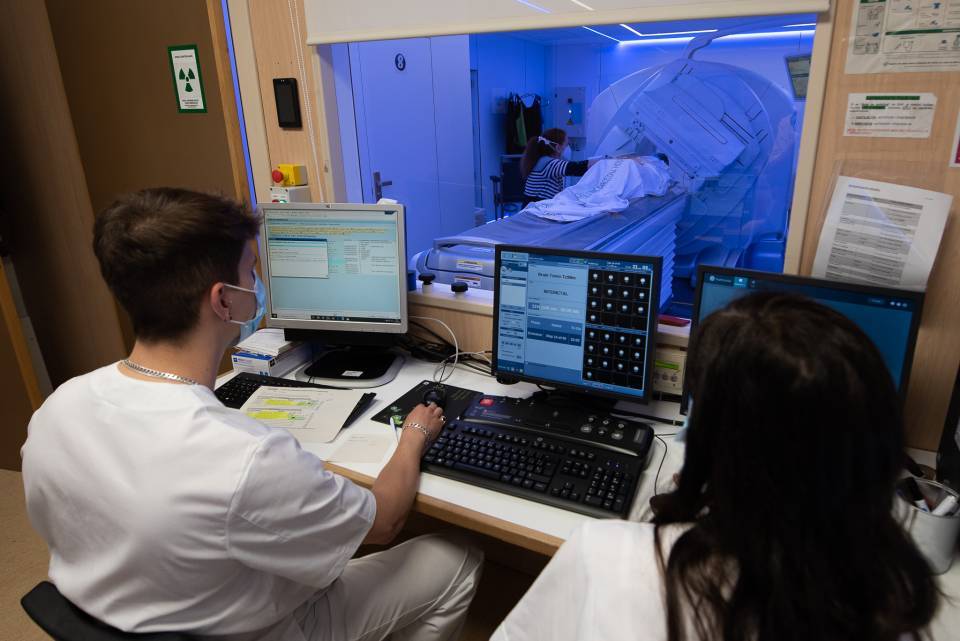
At the Hospital Clínic Barcelona’s Diagnostic Imaging Centre, thousands of medical images are generated every day from various techniques and modalities such as X-ray, ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), positron emission tomography (PET-CT) or single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT-CT), among others. The qualitative analysis (for example, detecting lesions in organs or systems) or quantitative analysis (such as determining the volume of a lesion) of these images is a complex, time-consuming task that is often subject to variability among professionals.
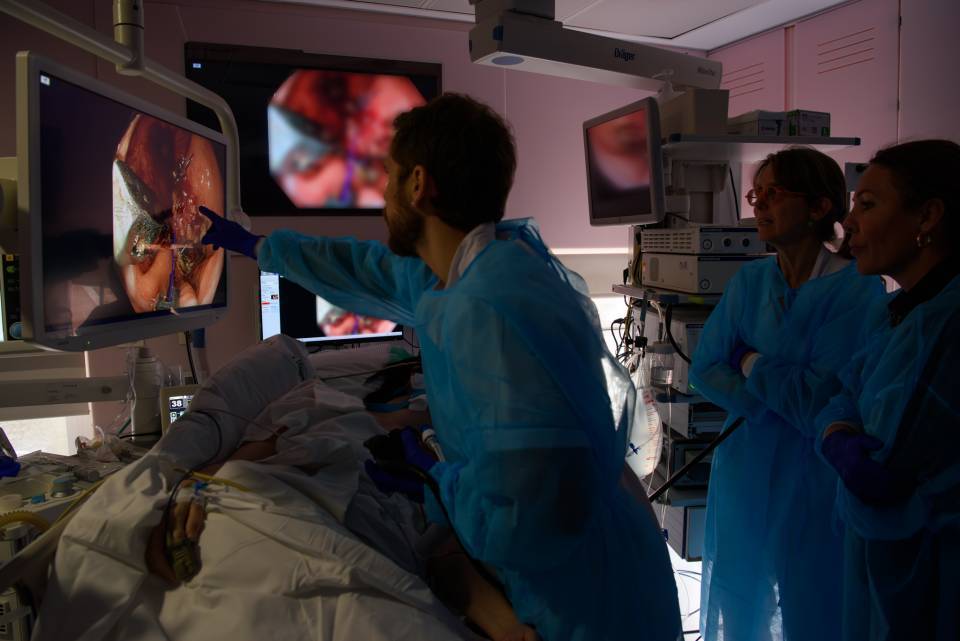
In this regard, AI plays a fundamental role given its ability to analyse images and large volumes of data in a very short time. Machine learning algorithms, and more specifically deep learning neural networks, are trained to recognize patterns in images, often with diagnostic or prognostic impact, that might go unnoticed by the human eye. These methodologies enhance anomaly detection with a precision comparable to that of experienced specialists, accelerating diagnostic response times, contributing to better resource management, and reducing the workload of medical professionals. In this sense, AI is not expected to replace the specialist, but rather to complement them.
AI's learning is continuous and often exponential. Its development and refinement are determined by the quality and quantity of the clinical and imaging data used, allowing it to adapt to different pathologies, imaging techniques, or specific populations.
AI will improve the personalization of treatments, as it allows for the identification of correlations and predictions among imaging data, a multitude of clinical variables, and omics data, through medical history or laboratory test results. This aspect will enhance predictive and preventive medicine, improving patients' quality of life and reducing healthcare system costs.
How AI will be integrated into the Clínic's Diagnostic Imaging Centre
The integration of AI into the Clínic's Diagnostic Imaging Centre is progressive.
However, this evolution is not without challenges. It will be necessary to ensure the security, privacy, and ethics of data use, as well as rigorous clinical validation before its application and implementation. It will also be essential to train and familiarize healthcare professionals with the use of these new tools in a judicious and confident manner.
Finally, AI will allow for the development of new projects and research areas at the Diagnostic Imaging Centre with a potential impact on all sections.
In conclusion, AI has great potential in the field of diagnostic imaging. If its integration is carried out responsibly and collaboratively, it can become an ally in improving the efficiency and quality of care and the healthcare system.